💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
通过调用图像来重建新影片及计算颜色通道的平均灰度值,并检测帧与前一帧之间的差异
本文展示了一种从视频中提取帧并获取帧的方法,并且可以选择将单个帧保存到单独的图像文件中。接着,我们可以通过从磁盘调用保存的图像来重建新的影片。此外,我们还介绍了如何计算颜色通道的平均灰度值,并检测每一帧与前一帧之间的差异。
为了实现这些功能,我们使用了VideoReader和VideoWriter类。VideoReader类允许我们从视频文件中读取帧,并且可以指定读取的起始和结束时间。通过使用该类,我们可以轻松地获取视频中的每一帧。
接下来,我们可以选择将每一帧保存为单独的图像文件。这可以通过使用imwrite函数来实现。我们可以为每一帧指定一个文件名,并将其保存到指定的目录中。这样,我们就可以将视频拆分成单独的图像文件,方便后续处理或者用于其他用途。
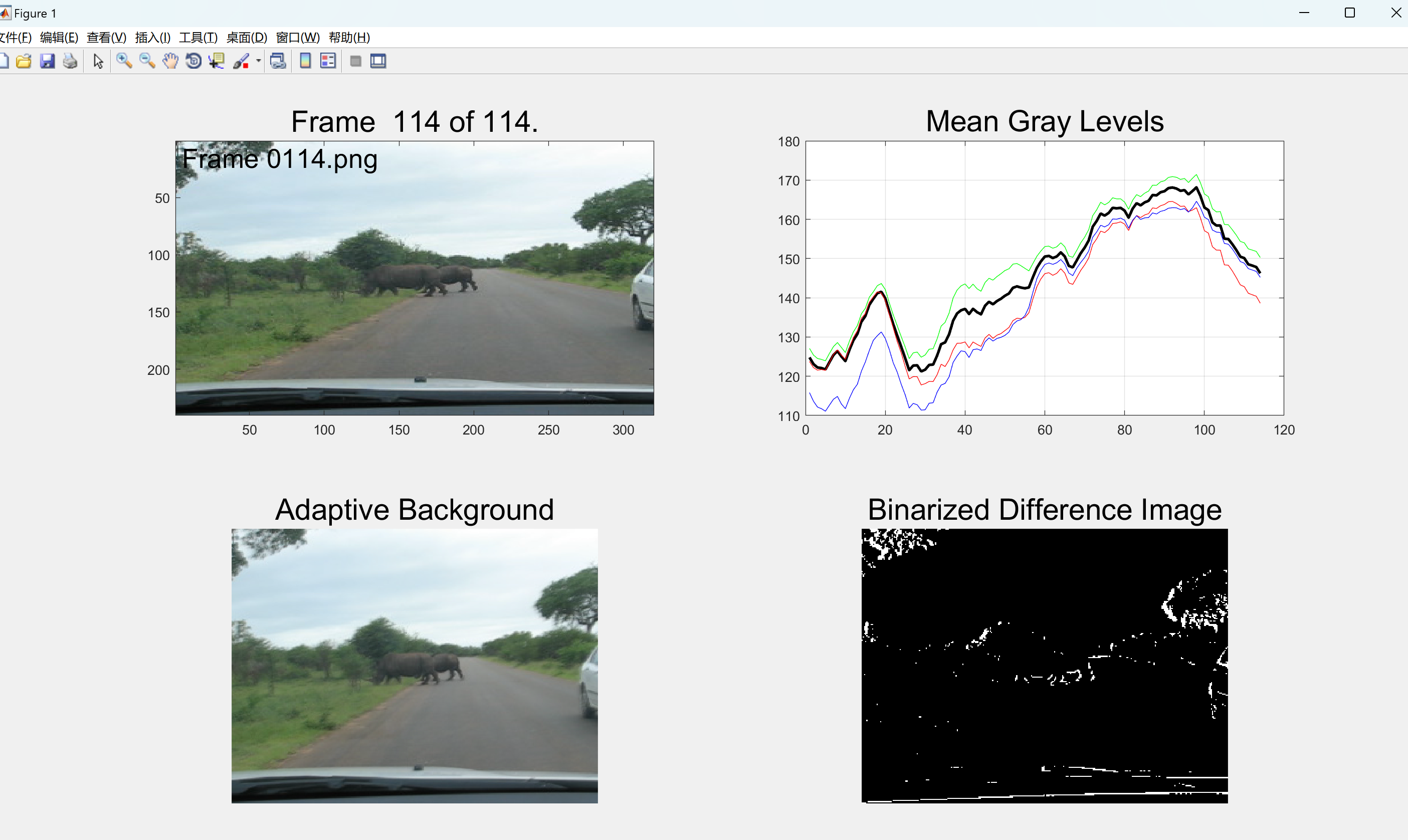
另外,我们还可以计算颜色通道的平均灰度值。通过将每个像素的RGB值转换为灰度值,并计算所有像素的平均值,我们可以得到整个图像的平均灰度值。这个值可以用来描述图像的整体亮度。
最后,我们还可以检测每一帧与前一帧之间的差异。通过对比相邻帧的像素值,我们可以计算出它们之间的差异。这可以用来检测视频中的运动或者其他变化情况。例如,我们可以通过比较两个相邻帧的差异来检测物体的移动或者背景的变化。
综上,本文介绍了如何使用VideoReader和VideoWriter类来提取视频帧,并展示了如何保存单个帧作为图像文件。此外,我们还讨论了如何计算颜色通道的平均灰度值,并检测每一帧与前一帧之间的差异。这些技术可以在图像处理和视频分析领域中发挥重要作用。
📚2 运行结果
运行视频:
部分代码:
% Write the image array to the output file, if requested.
if writeToDisk
% Construct an output image file name.
outputBaseFileName = sprintf('Frame %4.4d.png', frame);
outputFullFileName = fullfile(outputFolder, outputBaseFileName);
% Stamp the name and frame number onto the image.
% At this point it's just going into the overlay,
% not actually getting written into the pixel values.
text(5, 15, outputBaseFileName, 'FontSize', 20);
% Extract the image with the text "burned into" it.
frameWithText = getframe(gca);
% frameWithText.cdata is the image with the text
% actually written into the pixel values.
% Write it out to disk.
imwrite(frameWithText.cdata, outputFullFileName, 'png');
end
% Calculate the mean gray level.
grayImage = rgb2gray(thisFrame);
meanGrayLevels(frame) = mean(grayImage(:));
% Calculate the mean R, G, and B levels.
meanRedLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 1)));
meanGreenLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 2)));
meanBlueLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 3)));
% Plot the mean gray levels.
hPlot = subplot(2, 2, 2);
hold off;
plot(meanGrayLevels, 'k-', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold on;
plot(meanRedLevels, 'r-');
plot(meanGreenLevels, 'g-');
plot(meanBlueLevels, 'b-');
grid on;
% Write the image array to the output file, if requested.
if writeToDisk
% Construct an output image file name.
outputBaseFileName = sprintf('Frame %4.4d.png', frame);
outputFullFileName = fullfile(outputFolder, outputBaseFileName);
% Stamp the name and frame number onto the image.
% At this point it's just going into the overlay,
% not actually getting written into the pixel values.
text(5, 15, outputBaseFileName, 'FontSize', 20);
% Extract the image with the text "burned into" it.
frameWithText = getframe(gca);
% frameWithText.cdata is the image with the text
% actually written into the pixel values.
% Write it out to disk.
imwrite(frameWithText.cdata, outputFullFileName, 'png');
end
% Calculate the mean gray level.
grayImage = rgb2gray(thisFrame);
meanGrayLevels(frame) = mean(grayImage(:));
% Calculate the mean R, G, and B levels.
meanRedLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 1)));
meanGreenLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 2)));
meanBlueLevels(frame) = mean(mean(thisFrame(:, :, 3)));
% Plot the mean gray levels.
hPlot = subplot(2, 2, 2);
hold off;
plot(meanGrayLevels, 'k-', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold on;
plot(meanRedLevels, 'r-');
plot(meanGreenLevels, 'g-');
plot(meanBlueLevels, 'b-');
grid on;
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]金黎明,周晓光,苏志远.一种基于帧间差分背景重建的动目标检测算法[C]//2009年先进光学技术及其应用研讨会.0[2023-09-21].
[2]袁建英.序列图像光流计算关键技术研究及其在三维重建中的应用[D].西南交通大学,2015.DOI:CNKI:CDMD:1.1016.166603.
[3]王静婷,李慧斌.单张图像三维人脸重建方法综述[J].计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(17):1-21.DOI:10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2210-0041.